Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer ICD 10 is C79.9.
Tap “Watch Now” for an easy-to-understand overview of Stage 4 Melanoma.
- Stage 4 Melanoma
Overview
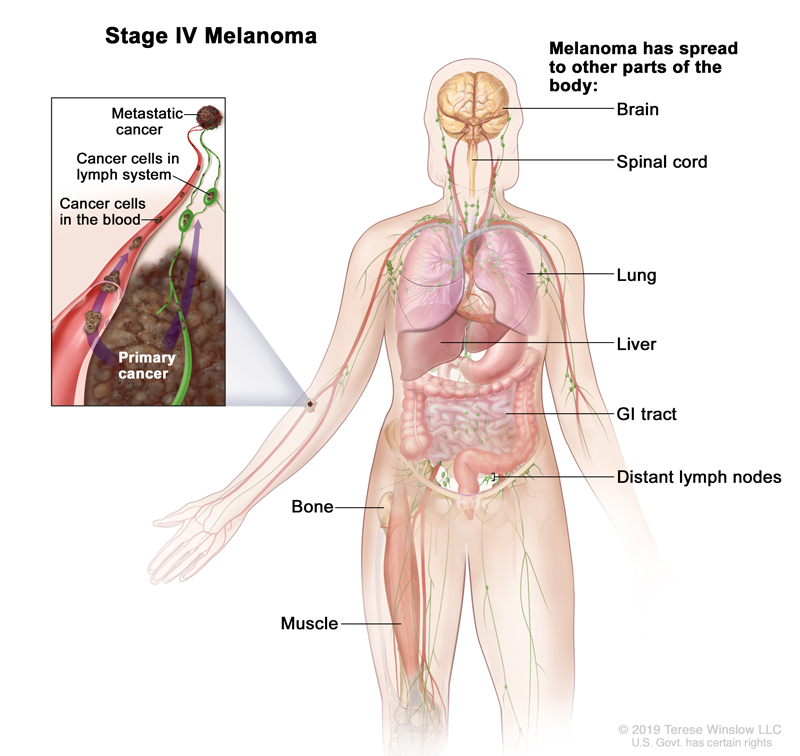
A Stage 4 Melanoma diagnosis means that the cancer has spread beyond your skin and closest lymph nodes, shown here in green, to distant organs in your body.
Common places the cancer spreads to are your brain, lungs, bones, liver, spinal cord, bone, soft tissue, including your muscles, your stomach and/or your distant lymph nodes.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type and BRAF mutation, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you. BRAF mutation is present in 40-60% of all melanoma patients.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-melanoma
Recommended Melanoma Cancer Videos
Understanding Melanoma
Causes, Staging & More
What Are The Stages of Melanoma?
Melanoma expert Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD,

How Cancer Spreads
Metastastis

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Stage 4 Melanoma Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 4 Melanoma Symptoms
- A for asymmetry
- B for borders (uneven)
- C for color (multiple colors in one mole)
- D for diameter (larger than 6mm)
- E for evolving (size, shape, color, elevation of a spot on your skin)
Source: Skincancer.org
Stage 4 Melanoma Definition
Source: AimatMelanoma.org
Stage 4 Melanoma Recurrence Rate
Source: AimatMelanoma.org
Stage 4 Melanoma Prevention
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Limit time in the sun, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV radiation is strongest. Seek shade whenever possible.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin, and reapply every two hours and after swimming or sweating.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Use hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing to shield your skin from UV radiation. Avoid Tanning Beds: Do not use tanning beds or other artificial sources of UV light, as they increase the risk of melanoma.
- Perform Regular Skin Checks: Conduct monthly self-exams to monitor your skin for new or changing moles or spots, noting any changes in size, shape, or color.
- Regular Dermatologist Visits: Have regular skin exams by a dermatologist, especially if you have a personal or family history of melanoma, numerous moles, or a history of severe sunburns.
Source: AimatMelanoma.org
Stage 4 Melanoma Treatment
Source: AimatMelanoma.org














