- Extensive Stage SCLC Lung Cancer
Overview
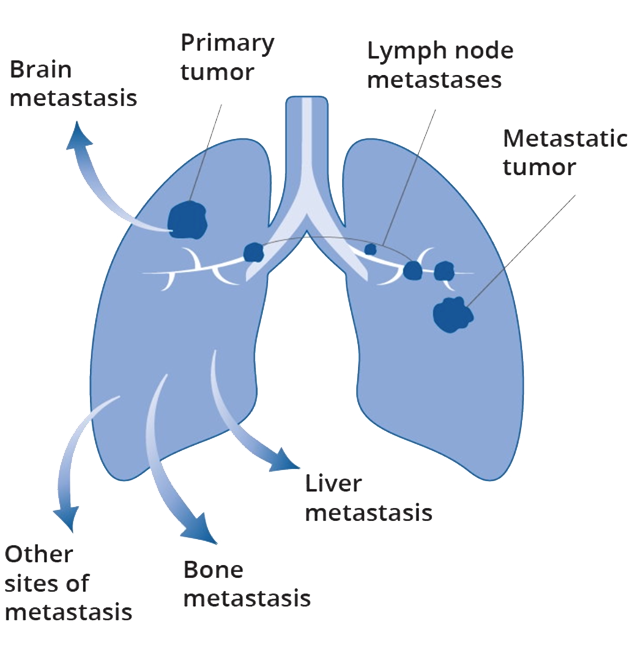
Extensive Stage SCLC means that the tumor has affected both lungs or any other organ in your body, making it difficult to be treated with surgery or radiotherapy.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-lung
Recommended Lung Cancer Videos
SCLC & Immunotherapy
Is Immunotherapy Right for Me?
Treatment & Management of SCLC
Understand Your Treatment Options

How Does Cancer Spread?
What Does Metastastis Mean?

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It!
Reduce Your Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Extensive Stage Lung Cancer Symptoms
- Breathlessness
- Chronic cough
- Feeling weak
- Coughing up blood
- Noisy breathing
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- Horner’s Syndrome(drooping of the eyelid and absence of sweating on one side of the face)
- Yellowing of the eyes and skin due to the spread to the liver
- Superior vena cava syndrome causes swelling of the face and upper part of the body due to obstruction from the tumor
Source: Cancer.org
Extensive Stage Lung Cancer Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Therapy that targets receptors in the lungs such as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors can be done. Other mutations such as ALK, BRAF, MET, NTRK, RET and ROS-1 have specific targeted therapy that deals with the mutation.
- Immunotherapy helps a person’s immunity identify and kill lung cancer. It can be done with or without chemotherapy.
- Radiotherapy
Source: Cancer.org
Extensive Stage lung Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Extensive Stage Lung Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.org
Extensive Stage Lung Cancer Prevention
- Avoid Smoking: The most effective way to prevent lung cancer is to never smoke. If you currently smoke, quitting significantly reduces your risk.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Minimize exposure to secondhand smoke to decrease risk.
- Reduce Exposure to Carcinogens: Limit exposure to known carcinogens such as asbestos and radon. Ensure proper ventilation and use protective equipment if you work with hazardous substances.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a diet rich in fruits and vegetables to support overall lung health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support overall health.
- Regular Screenings: For individuals at high risk (e.g., heavy smokers or those with a family history of lung cancer), consider regular screenings with low-dose CT scans to detect lung cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage.
Source: Cancer.org
Extensive Stage Lung Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Cancer.org














