- Billiary Tract Resectable Liver Cancer
Overview
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer is when the cancer is found only in the gallbladder or bile ducts, making it accessible and removable through surgery.
It also means that the tumor has not affected any nearby structures or other organs.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
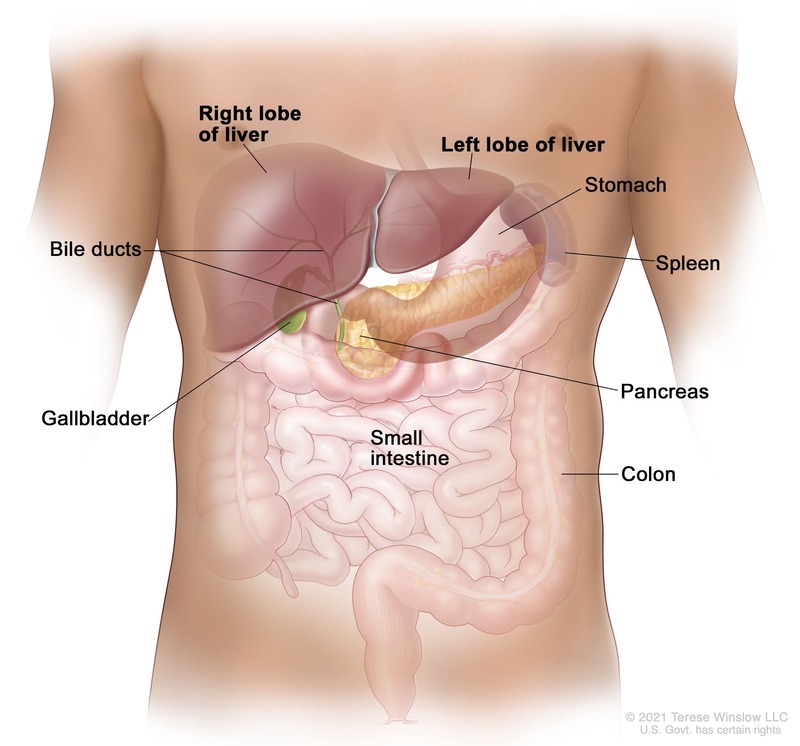
Cancer Research U.K. CC BY-SA 4
Recommended Liver Cancer Videos

Liver Cancer In 4 Minutes
Hear from Doctor Sachin MODI

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Symptoms
- Yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice) and pale stool
- Feeling weak constantly
- An abnormal swollen abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unintentional weight loss
- A lump on the right side below the rib cage
Source: Cancer.gov
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Treatment
- Surgery to remove your cancer which may include a partial hepatectomy that means part of your liver is removed.
- Surgery to remove your cancer which may include a partial hepatectomy that means part of your liver is removed
- A stent is placed to direct bile out of the body.
- Surgery to remove your cancer which may include a partial hepatectomy that means part of your liver is removed or the whipple procedure may be done.
- A stent is placed to direct bile out of the body.
Source: Cancer.gov
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.gov
Resectable Bile Duct Cancer Prevention
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Properly manage chronic liver diseases and infections, such as hepatitis B and C, which increase the risk of bile duct cancer.
- Avoid Alcohol: Limit or avoid alcohol consumption to prevent liver damage and lower cancer risk.
- Healthy Diet and Weight Management: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and maintain a healthy weight. Limit consumption of red and processed meats.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco use, as smoking is a risk factor for various cancers, including bile duct cancer.
- Protect Against Hepatitis Infections: Get vaccinated against hepatitis B and take precautions to avoid hepatitis C infection.
- Limit Exposure to Carcinogens: Reduce exposure to harmful chemicals and substances that could increase cancer risk.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular check-ups and screenings are important for individuals with liver disease or other risk factors to monitor liver health and detect any potential issues early.
Source: Cancer.gov














