- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Overview
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. It usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of Leukemia in adults. It often occurs during or after middle age; it rarely occurs in children.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health and confirm your diagnosis.
In some cases a lymph node biopsy and or bone marrow biopsy may be performed to obtain more information about your diagnosis.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed. This information is critical to finding the best treatment option for you given your goals and lifestyle needs.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
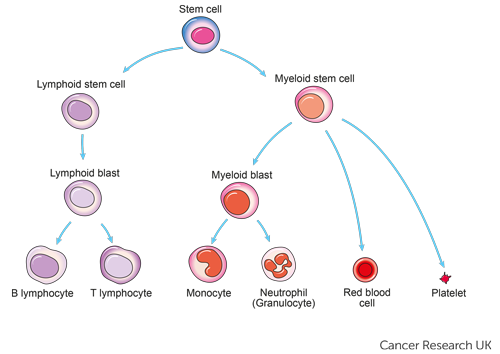
National Institute of Health/ treatment-leukemia
Recommended Leukemia Cancer Videos
What Is Blood Cancer
Brought To You By Black Health Matters
Leukemia Causes, Signs and Symptoms
What is Leukemia?

How Cancer Spreads
Metastastis

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Symptoms
- Painless swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, underarm, stomach, or groin
- weakness or feeling tired
- pain or a feeling of fullness below the ribs
- fever and infection
- easy bruising or bleeding
Source: www.cancer.gov
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy with bone marrow or peripheral stem cell transplant
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Watchful waiting
Source: www.cancer.gov
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Recurrence Rate
- For Patients in Remission: Even after successful treatment, CLL often recurs. Studies suggest that CLL may return in a significant number of patients, with estimates ranging from 30% to 70% depending on factors such as the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of the initial treatment.
- Relapse Risk: The risk of relapse is higher in patients with more aggressive forms of CLL or those who have been treated with less effective therapies.
Source: www.cancer.gov
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Definition
Source: www.cancer.gov
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Prevention
- Avoid Exposure to Known Carcinogens: Reduce exposure to harmful substances like certain chemicals and pesticides.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity.
- Avoid Smoking: Do not smoke, as tobacco use is linked to various cancers.
- Manage Existing Health Conditions: Effectively manage any chronic health conditions that may contribute to cancer risk.
Source: Cancer.gov















