- Stage 4A Bladder Cancer
- Stage 4B Bladder Cancer
Overview
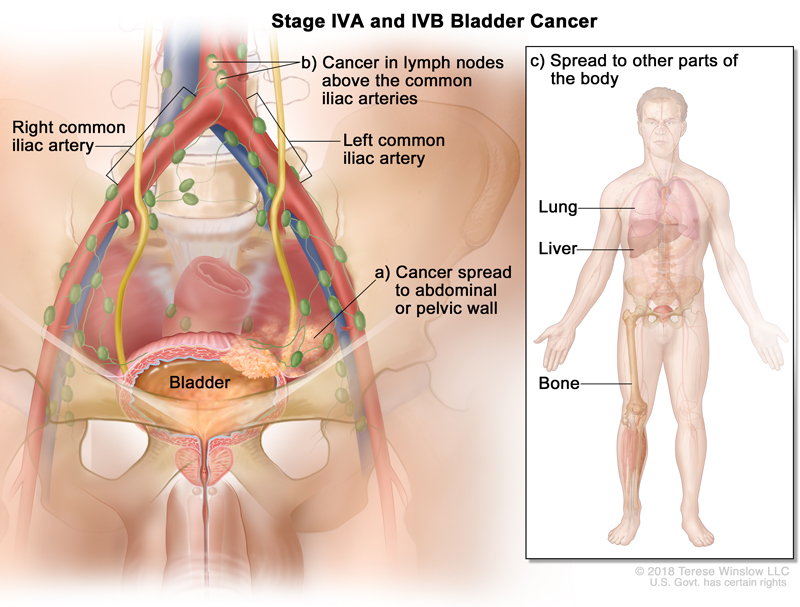
Stage 4A Bladder Cancer diagnosis means that the Cancer has either:
Spread to the wall of your abdomen or pelvis as indicated on the lower right by the letter a),
or
The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes that are above your common iliac arteries as noted by the letter b). These are the major arteries found on either side of your pelvis. The lymph nodes can be seen here at the top of the image in green.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Urine, Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is done through a biopsy to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy and, more recently, with immunotherapy.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-bladder
Overview
Stage 4B Bladder Cancer diagnosis means that the Bladder Cancer has spread from your bladder to other parts of your body such as the lung, liver or bones as shown here on the right.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Urine, Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is done through a biopsy to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy and, more recently, with immunotherapy.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.

National Institute of Health/ treatment-bladder
Recommended Bladder Cancer Diagnosis Videos
Understanding Your Bladder Cancer
An Easy to Follow Overview

Understanding Your Cancer Diagnosis
What Are Your Goals & More

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
- Blood in urine
- Urinating multiple times in a night
- Pain while urinating
- Difficulty urinating with a low-pressure stream of urine
- Pain in the abdomen
- Bone pain
- Weakness and lethargy
- Swelling of the legs
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (indicates spread to the liver)
- Difficulty breathing (indicates a possible spread to the lungs)
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Treatment
- Surgery to remove the whole bladder and surrounding structures that are affected.
- Surgery to divert urine as palliative treatment.
- Chemotherapy after surgery given directly into the bladder.
- External radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy helps the immune system identify and kill the Bladder Cancer. BCG is the most commonly used immunotherapy for this Stage.
- A Clinical trial with a new treatment.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Prevention
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking is the most significant risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products can greatly reduce the risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Limit Exposure to Carcinogens: If you work in environments with exposure to industrial chemicals (such as those used in the dye, rubber, or chemical industries), using proper protective equipment and following safety guidelines can help reduce your risk.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help flush out potentially harmful substances from the bladder and may lower the risk of bladder cancer.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, and managing a healthy weight contribute to overall well-being and may help lower cancer risk.
- Regular Screenings: For individuals at high risk of bladder cancer (e.g., those with a history of bladder cancer, significant exposure to risk factors), regular screenings and medical check-ups are important for early detection and management.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Conditions that cause chronic irritation or inflammation of the bladder, such as chronic urinary infections or interstitial cystitis, should be managed appropriately.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Definition
- Stage 4A: The cancer has spread to nearby structures, such as the prostate, uterus, or vagina, or to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 4B: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or lungs.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Cancer.gov















