Stage 3 Bladder Cancer ICD 10 is C67.3.
Tap “Watch Now” for an easy-to-understand overview of Stage 3 Bladder Cancer.
- Stage 3A Bladder Cancer
- Stage 3B Bladder Cancer
Overview
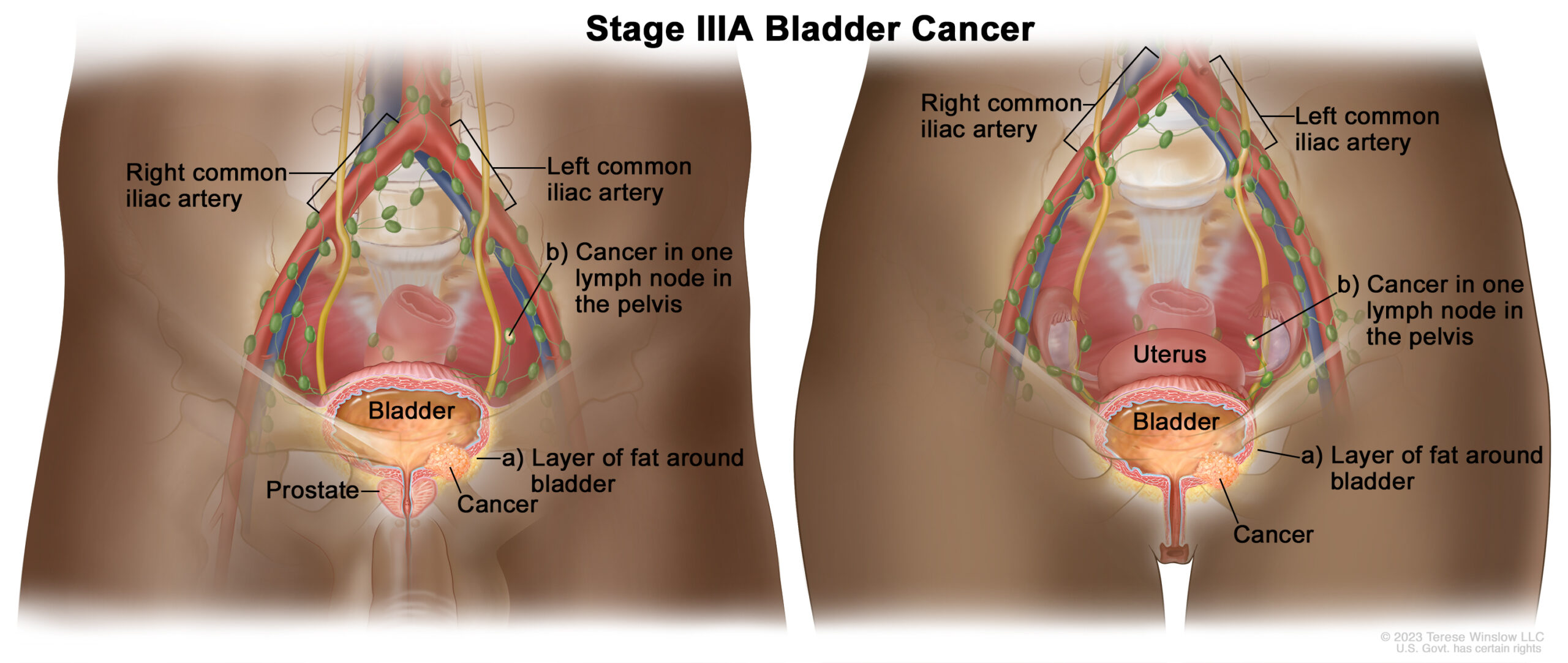
Stage 3A Bladder Cancer diagnosis means the Cancer has spread to one of the following areas of your body:
a. The layer of fat surrounding your bladder, shown here in yellow, and may have spread to nearby organs like uterus and vagina in women or seminal vesicles and prostate in men but has not spread to your lymph nodes.
or
b. the cancer has spread to one lymph node in the pelvis area, shown here in green.
In Stage 3A Bladder Cancer, the cancer has not spread to any other organs in your body.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Urine, Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done through a biopsy to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-bladder
Overview
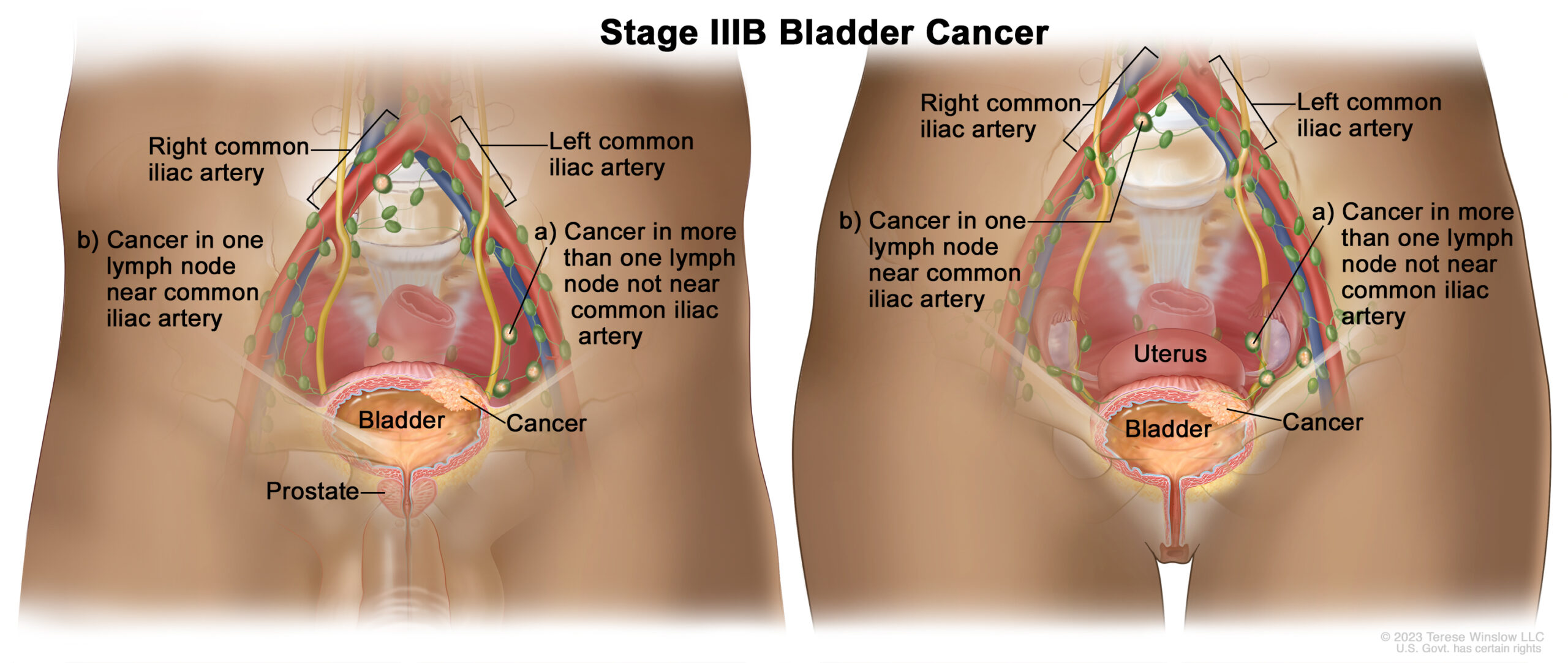
Stage 3B Bladder Cancer diagnosis means the Cancer has spread to:
a) More than one lymph node in the pelvis, shown in green in your pelvic area
or
b) One or more lymph nodes outside the pelvis, but inside the abdomen.
In Stage 3B Bladder Cancer, the cancer has not spread to any other organs in your body.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Urine, Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done through a biopsy to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
Replay this audio as often as needed and then take a look at our Commonly Searched Questions below.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-bladder
Recommended Bladder Cancer Videos
Understanding Your Bladder Cancer
An Easy to Follow Overview

Understanding Your Cancer Diagnosis
What Are Your Goals & More

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
- Blood in urine
- Urinating multiple times in a night
- Pain while urinating
- Difficulty urinating with a low-pressure stream of urine
- Pain in the abdomen
- Weakness and lethargy
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Treatment
- Surgery to remove the Bladder Cancer through the tube that carries urine from the bladder (urethra)
- Surgery to remove the whole bladder and the surrounding area that is affected
- Chemotherapy after surgery given directly into the bladder
- External radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy helps the immune system identify and kill the Bladder Cancer. BCG is the most commonly used immunotherapy for this Stage
- A Clinical trial for a new treatment
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Prevention
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking is the primary risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products can significantly decrease the risk of bladder cancer.
- Limit Exposure to Carcinogens: If you are exposed to chemicals known to increase bladder cancer risk (such as those in the dye, rubber, or chemical industries), use protective measures and adhere to safety regulations to reduce exposure.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking adequate amounts of fluids, particularly water, can help dilute and flush potential carcinogens from the bladder.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can promote overall health and potentially lower cancer risk.
- Regular Health Check-ups: For individuals with a history of bladder cancer or those at high risk, regular check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection and management.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Cancer.gov














