Stage 1 Breast Cancer ICD 10 is C50.919.
Tap “Watch Now” below for an easy-to-understand overview and then compare your treatment options side-by-side so you can help your doctors find the best option for you.
- Stage 1A Breast Cancer
- Stage 1B Breast Cancer
- Understanding HR+, HER2, TNBC
Overview
Stage 1A Breast Cancer is when the cancer is found only in your breast and is 2 centimeters or smaller, about the size of a peanut. In Stage 1A Breast Cancer, the cancer has not spread to your lymph nodes, shown here in green, or to any other organs in your body.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify your cancer sub-type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you. The most common Breast Cancer sub-types are Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Positive and Triple Negative (TNBC).
You may also require Saliva or Blood Analysis to look for specific mutations (actual changes in your body’s DNA), called BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now” to help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment and what side-effects you may experience.
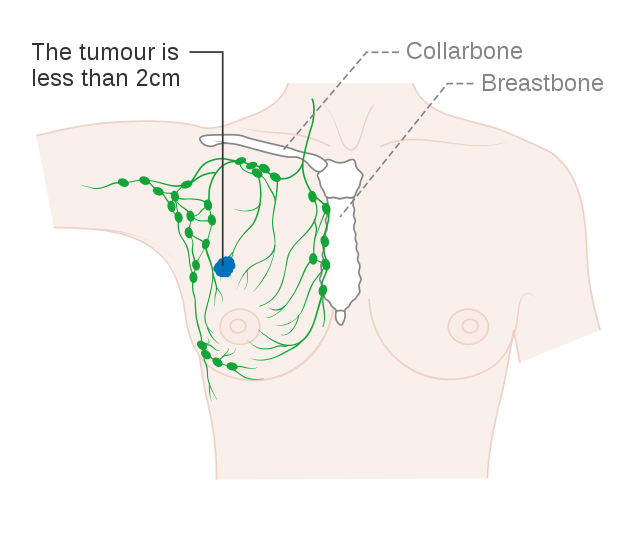
Cancer Research U.K. CC BY-SA 4
Overview
A Stage 1B Breast Cancer diagnosis is when your tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters and may have formed small clusters of cancer cells in your lymph nodes.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify your cancer sub-type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you. The most common Breast Cancer sub-types are Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Positive and Triple Negative (TNBC).
You may also require special Saliva or Blood Analysis to look for specific mutations (actual changes in your body’s DNA), called BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now” to help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment and what side-effects you may experience.
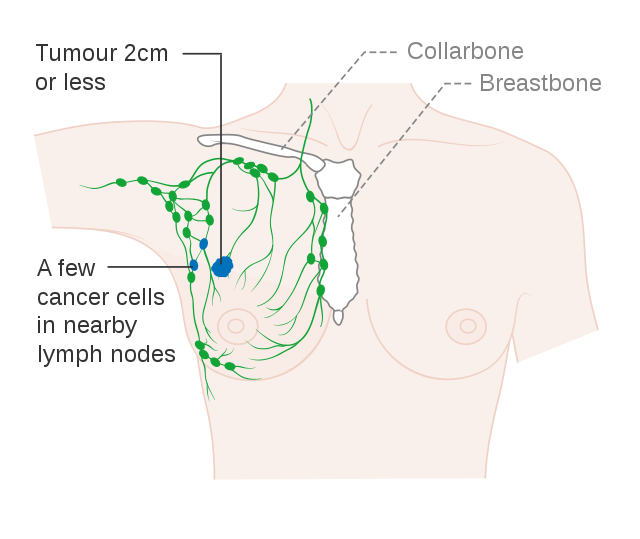
Cancer Research U.K. CC BY-SA 4
Your Status is critical to identifying the best treatment option for you
In addition to the size and cancer stage, your treatment options are guided by your Hormone Receptor status (+ or -) and HER2 status. Status is identified by analyzing cancer cells taken from the tumor in your breast, a procedure called a Biopsy.
HR-positive (HR+)
An HR+ diagnosis means that hormones are fueling the tumor. To understand your specific sub-type, your doctors will look for Estrogen Receptors (ER) and Progesterone Receptors (PR), your tumor can have one, both or neither.
About 70% of breast cancers are HR+.
If you test positive for HR, it means that your treatment should include medications that block hormone production.
HER2-positive (HER2+)
HER2 is a protein that is found in normal cells, it gives cells a signal to grow and produce more cells. A HER2 positive (+++) breast cancer diagnosis means that the tumor cells have too many HER2 proteins, causing uncontrolled tumor cell division, tumor growth and spreading.
About 15% of all breast cancer tumors are HER2 positive (+++). Some patients with HR+ can also have HER2 positive (+++).
If you test HER2+, it means that your treatment should include medications that block the HER2 protein to stop tumor cell growth.
TNBC Triple Negative Breast Cancer
“TNBC, or Triple-Negative Breast Cancer, is a breast cancer type that lacks the three receptors (proteins) commonly found in other breast cancer types:
1. estrogen receptors 2. progesterone receptors, and 3. HER2 protein receptors.
Given TNBC’s uniqueness, treating TNBC requires a different treatment approach then those used to treat other types of breast cancer.
TNBC accounts for about 10-15% of all breast cancers and tends to be more aggressive then other breast cancers.
Recommended Breast Cancer Videos

Stage 1 Breast Cancer
A Helpful Introduction from Dr. Jennifer Griggs

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Answers To The Most Searched Questions
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Treatment
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Symptoms
- a breast lump or tissue thickening that feels different from surrounding tissue and is new
- breast pain
- red or discolored, pitted skin on the breast
- swelling in all or part of your breast
- a nipple discharge other than breast milk
- bloody discharge from your nipple
- inverted nipple
Source: Healthline.com
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Prevention
- Regular Screening: Adhere to mammogram guidelines.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise, and eat a balanced diet.
- Limit Alcohol: Consume no more than one drink per day.
- Avoid Tobacco: Do not smoke.
- Manage Hormones: Discuss the risks of hormone replacement therapy with your doctor.
- Genetic Counseling: For high-risk individuals, consider genetic testing and preventive measures.
Source: Cancerresearchuk.org
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Cancer.org













