- Stage 0 Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Overview
When diagnosed with Stage 0 Breast Cancer, it is described as pre-cancer or non-invasive. The most common form of noninvasive cancer is called ductal carcinoma in situ or DCIS.
With a Stage 0 Breast Cancer diagnosis, there is no evidence that cancer cells have spread into other tissues and abnormal cells are found only in the place where they first originated.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify your cancer sub-type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you. Stage 0 Breast Cancer is treated depending on wether the tumor has Hormone Receptors positive or negative.
You may also require Saliva or Blood Analysis to look for specific mutations (actual changes in your body’s DNA), called BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now” to help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment and what side-effects you may experience.
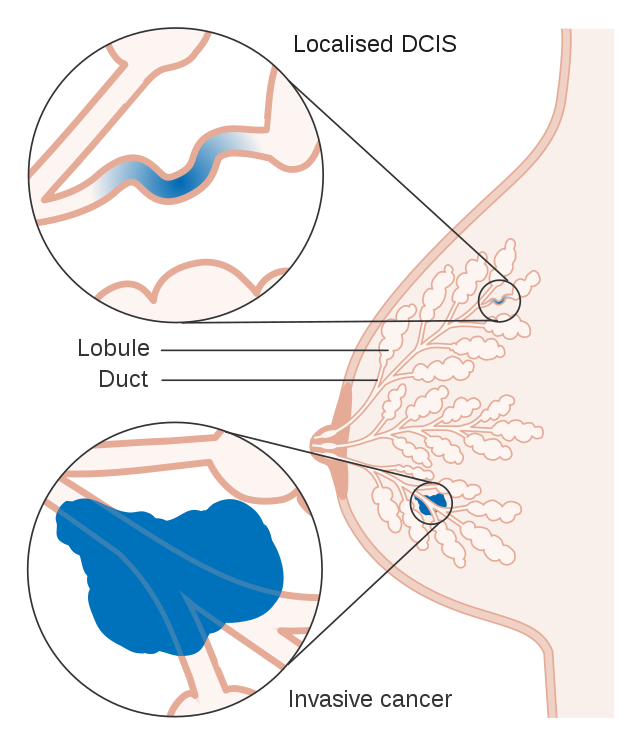
Cancer Research U.K. CC BY-SA 4
Recommended Breast Cancer Diagnosis Videos

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Answers to the Most Searched Questions
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Treatment
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Breastcancer.org
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Breastcancer.org
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Symptoms
Source: Mayoclinic.org
Stage 0 Breast Cancer Prevention
- Regular Screening: Follow recommended mammogram guidelines.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and eat a balanced diet.
- Limit Alcohol: Keep alcohol consumption to no more than one drink per day.
- Avoid Tobacco: Do not smoke.
- Manage Hormone Use: Discuss hormone replacement therapy options with your doctor.
- Genetic Counseling: For those with a strong family history, consider genetic testing and preventive measures.
Source: Mayoclinic.org