Non Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Non Metastatic Prostate Cancer also called Regional Prostate Cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate and has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Understanding your regional prostate cancer diagnosis will help you partner with your doctors to make the best treatment choice for you.Regional Prostate Cancer ICD 10 is C61.
Tap “Watch Now” for an easy-to-understand overview of non-metastatic prostate cancer.
- Regional Prostate Cancer
- Gleason Score & PSA Explained
Overview
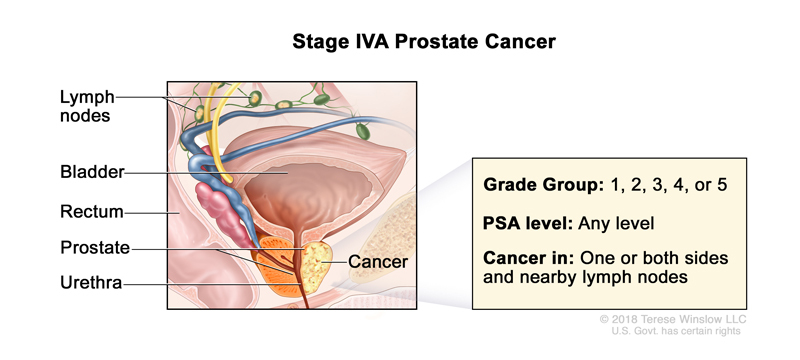
A Regional Prostate Cancer diagnosis, also known as Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer or Stage 4A Prostate Cancer, means that the cancer has spread to the closest lymph nodes in your pelvis shown at the top of the image in green. It has not spread to any other organs in your body.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue Analysis is done to identify the prostate cancer cell type and the Gleason Score, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
At Stage 4A, your PSA can be found at any level and your Gleason Score can range from 2-10, Grade Group 1-5.
You may also require special Saliva or Blood Analysis to look for specific mutations, actual changes in your body’s DNA, called BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
Cancer Research U.K. CC BY-SA 4
Gleason Score & PSA Density
A Prostate Cancer diagnosis is based upon the results of staging and two tests called the Gleason Score and the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests
Finding Your Gleason Score
Samples of your cancer cells are examined to find out your Gleason Score. A Gleason Score, which will range between 2 and 10, describes how aggressive a prostate tumor is by looking at how similar or different the cancer cells look to healthy cells.
The Gleason Score is made up of 2 grades that range from 1 to 5. A low grade of 1 means that the cells in the tumor look very much like healthy prostate cells. Cells that look completely different to normal cells are assigned a higher score, usually 4 or 5.
- The first grade is given to describe the cells in the largest area of the tumor
- The second grade is given to describe the cells in the second largest area of the tumor.
When these two grades are added together, they give us a Gleason Score between 2 and 10. For example, 3+4 = Gleason Score 7.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) tests
Your Dr. also measures PSA Density to help determine the aggressiveness of the prostate cancer found. PSA Density is your PSA level, divided by the volume of the prostate gland.
A high PSA density is often a predictor of Prostate Cancer but please discuss your specific situation with your doctors.
Replay this Audio as often as needed and then take a look at our Commonly Searched Questions below.
Recommended Prostate Cancer Videos
Prostate Cancer
An Overview
Understanding Localized Prostate Cancer
An Overview

Prostate Cancer In The Black Community
Brought To You By Black Health Matters

A Diagnosis and Treatment: Localized Prostate Cancer
A Conversation with Dr. John Lynch

Exercise & Prostate Cancer
From Your Friends @ the Oncology Nursing Society

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced
Commonly Searched Questions
Regional Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
Source: Cancer.gov
Regional Prostate Cancer Definition
Source: Cancer.org
Regional Prostate Cancer Treatment
- Radiation therapy (RT) with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT)
- Radical prostatectomy
Source: Uptodate.com
Regional Prostate Cancer Recurrence Rate
Source: Pasadenacyberknife.com
Regional Prostate Cancer Symptoms
- burning or pain when urinating
- trouble starting or ending urination
- weak leak
- urge to pee during the night
- frequent urination
Source: Urologyhealth.org
Regional Prostate Cancer Prevention
- Healthy Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limit high-fat foods, especially from animal sources.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
- Avoid Smoking: Do not smoke and avoid exposure to tobacco smoke.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether.
- Regular Check-ups: Discuss with your doctor about regular screenings and tests if you are at higher risk, such as having a family history of prostate cancer.
Source: Urologyhealth.org














